some principles of critical pedagogy
- horizontal, reciprocal rather than top-down, hierarchical “banking” method
- collaborative rather than competitive
- problem-posing and dialogic
- everybody brings knowledge; educator acts as coordinator to bring this out
- seeks to develop critical consciousness of one’s relationship to power structures
- uncovers the “hidden curriculum” of dominant educational institutions
- empowers the voices of everyday people to challenge “culture(s) of silence”
- whole body: mind/spirit/heart/feelings; this includes “social-emotional”
- oriented towards praxis, social change
1. Freire, P. (2000). Pedagogy of the oppressed (M.B. Ramos, Trans.) (30th anniversary edition). New York: Continuum Books. Ch. 2, read first 11 paragraphs up to [Footnote #1: Simone de Beauvoir…
2. Paulo Freire and the Development of Critical Pedagogy 4.56
3. Four Steps to Liberation: Paulo Freire and Pedagogy of the Oppressed 4.40
4. Maryellen Weimer. Critical Pedagogy Brings New Teaching and Learning Challenges. Teaching and Learning. December 8, 2009.
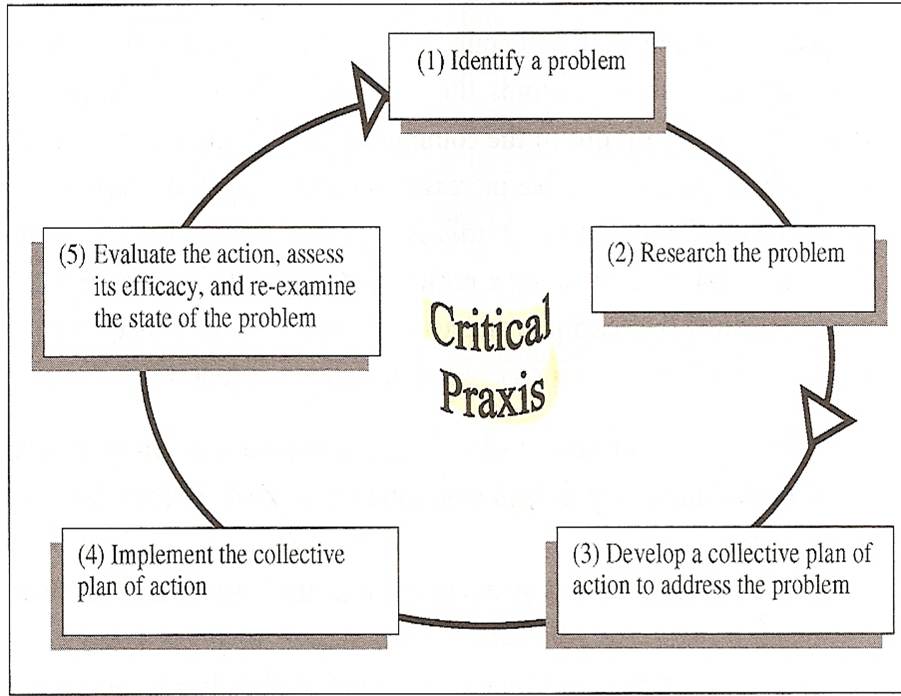
praxis cycle