Our research activities and plans for new research initiatives on the ATLAS experiment have been rewarded with several new grants. These are summarized in a news story published on 8 Dec 2022: Press Release.
All posts by Stephane Willocq
UMass team leads effort to measure the Higgs boson total width
A team led by Prof. Coelho Lopes de Sa, including Research Scientist William Leight, Postdocs Martina Javurkova and Michiel Veen, and Graduate Student Sam Krishnamurthy has produced first evidence for off-shell production of Higgs bosons. The analysis is based on 139 fb-1 of data collected with the ATLAS detector at the Large Hadron Collider during the years from 2015 to 2018. A sample of Higgs boson decays into pairs of Z bosons yielding final states with either 4 charged leptons (4l) or 2 charged leptons and 2 neutrinos (2l2v) was used to measure the off-shell Higgs production rate. A zero width is excluded for the first time with a significance greater than 3 standard deviations. The findings are summarized in a news item at https://atlas.cern/Updates/Briefing/Higgs-Total-Width and a complete description of the analysis is available as an ATLAS conference note.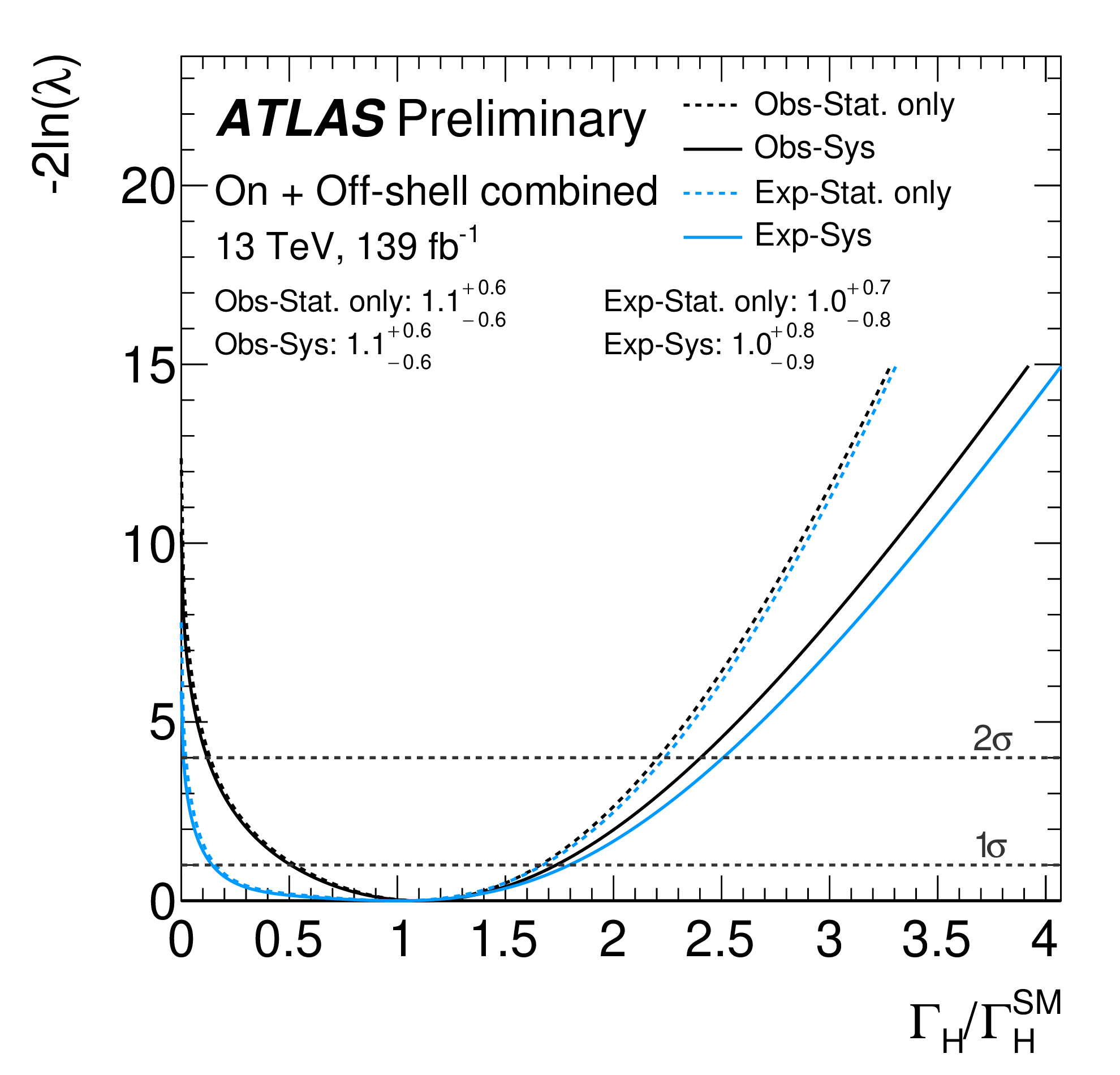
Prof. Verena Martinez Outschoorn earns tenure and promotion
Professor Verena Martinez Outschoorn has earned tenure and promotion to the rank of Associate Professor. Congratulations to Verena!
The news item from the Department of Physics can be viewed at https://www.physics.umass.edu/news/2020-12-07-verena-martinez-outschoorn-tenured-and-promoted.
Search for high-mass VH resonances in the fully hadronic channel with full Run 2 data
The results of a new search for high-mass VH resonances in the fully hadronic channel (qqbb) have been submitted for publication in Phys. Rev. D. The submitted paper and additional figures are available at https://atlas.web.cern.ch/Atlas/GROUPS/PHYSICS/PAPERS/HDBS-2018-11/. These results are the culmination of UMass student Zac Meadows’ graduate work and forms the basis of his PhD dissertation (CERN-THESIS-2020-062) under the direction of Prof. Willocq. Congratulations to Zac for a successful completion of this extensive work and a well-deserved PhD degree!
The analysis extends a previous search performed on 36 fb-1 of proton-proton collision data collected at sqrt(s) = 13 TeV with the full 139 fb-1 integrated luminosity collected between 2015 and 2018. Several improvements have been introduced to significantly increase the sensitivity of the search. These include: (i) more powerful W/Z tagging based on jets combining tracking and calorimeter measurements; (ii) variable-radius track jets to identify H -> bb decay; (iii) addition of the number of tracks associated with the Higgs candidate jet to suppress gluon-initiated jet background; (iv) boosted decision tree to correct kinematic biases in the data-derived background estimate.
The observed distributions of the WH and ZH candidate invariant masses are found to agree with the background prediction and upper limits are set on the cross section for production of W’ and Z’ bosons, in the context of the Heavy Vector Triplet (HVT) model. Several limits are shown below.


2019 US ATLAS Workshop Hosted at UMass-Amherst
The 2019 annual US ATLAS workshop will be held at UMass-Amherst from August 6 to August 9, 2019. The first day will be open to non-ATLAS members and will feature a broad set of talks by experts in the field of particle physics. A detailed agenda is available at https://indico.cern.ch/event/813845/.
Registration is required (see the agenda page). The second, third, and fourth days will be reserved to US ATLAS members only. Major aspects of the project will be presented and discussed. There will also be special sessions dedicated to hands-on tutorials, career planning, diversity and inclusion, discussions with representatives of grant agencies, etc.
See news item posted on the Department of Physics web site.
Pictures from the workshop are available at this link.
10th birthday of the Large Hadron Collider
Prof. Rafael Coelho Lopes de Sa wrote a news item about the 10th anniversary of the start of proton-proton collisions at the Large Hadron Collider, see the article at https://www.cns.umass.edu/news-events/news/happy-birthday-hadron-collider.
Two search articles submitted for publication: long-lived particles and diboson/dilepton combination
Two new search articles with major involvement by UMass members have been submitted for publication this week. The searches utilize the data collected with the ATLAS detector in 2015 and 2016, corresponding to up to 36 inverse femtobarns of pp collisions.
The first article is a search for long-lived particles decaying into muons. The search is sensitive to variants of Supersymmetry known as Gauge-mediated models as well as to rare decays of the Higgs boson into dark sector particles referred to as “dark photons”. The new particles produced travel measurable distances inside the detector before decaying into muons. 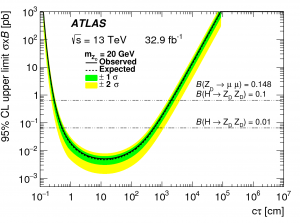 Those muons are then reconstructed by the ATLAS muon spectrometer and found to be inconsistent with originating from the pp collision point. Limits are set and new particles are excluded over a wide range of lifetimes (see figure). The article has been submitted to Phys. Rev. D, see https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.03057.
Those muons are then reconstructed by the ATLAS muon spectrometer and found to be inconsistent with originating from the pp collision point. Limits are set and new particles are excluded over a wide range of lifetimes (see figure). The article has been submitted to Phys. Rev. D, see https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.03057.
The second article is the result of a combination of about a dozen searches for heavy resonances decaying into pairs of W, Z, or Higgs bosons, as well as pairs of leptons. By combining many searches in different decay channels, the sensitivity to physics beyond the Standard Model is significantly increased and the complementarity between those searches allows us to set stronger constraints on the couplings between the heavy resonances and fermions, Higgs bosons, and W/Z bosons. 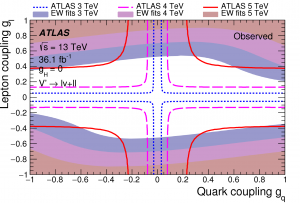 The constraints from this combination are stronger than those extracted from precise electroweak measurements in nearly the full coupling parameter space (see figure). The article has been submitted to Phys. Rev. D, see https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.02380.
The constraints from this combination are stronger than those extracted from precise electroweak measurements in nearly the full coupling parameter space (see figure). The article has been submitted to Phys. Rev. D, see https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.02380.
For more information, see https://atlas.web.cern.ch/Atlas/GROUPS/PHYSICS/PAPERS/EXOT-2017-03/ and https://atlas.web.cern.ch/Atlas/GROUPS/PHYSICS/PAPERS/EXOT-2017-31/.
Search for diboson resonances with jet substructure techniques
 A new LHC Run 2 search for diboson (WW, WZ and ZZ) resonances has been carried out with 37 inverse femtobarns of pp collisions collected by the ATLAS detector in 2015 and 2016. The search exploits jet substructure techniques to tag hadronic jets originating from the decay of W or Z bosons. The paper has been submitted to Phys. Lett. B, see http://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04445. Prof. Willocq, postdoctoral Research Associate Picazio and graduate student Meadows had responsibility for multiple aspects of the analysis (e.g. evaluating the boson-tagging performance, studying the modeling of the background, determining large-radius jet systematic uncertainties, etc.) and editing of the paper.
A new LHC Run 2 search for diboson (WW, WZ and ZZ) resonances has been carried out with 37 inverse femtobarns of pp collisions collected by the ATLAS detector in 2015 and 2016. The search exploits jet substructure techniques to tag hadronic jets originating from the decay of W or Z bosons. The paper has been submitted to Phys. Lett. B, see http://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04445. Prof. Willocq, postdoctoral Research Associate Picazio and graduate student Meadows had responsibility for multiple aspects of the analysis (e.g. evaluating the boson-tagging performance, studying the modeling of the background, determining large-radius jet systematic uncertainties, etc.) and editing of the paper.
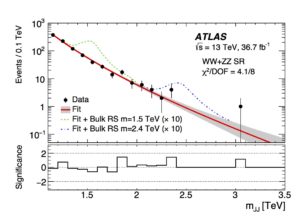
See the mass distribution for pairs of large-radius jets (figure on the right) with dashed curves showing the expected deviations in the presence of Kaluza-Klein excitations of the graviton, as predicted by the Randall-Sundrum model with one warped extra spatial dimension. Interpretations were also made in the context of a heavy scalar model and the heavy vector triplet model.
For more information, see https://atlas.web.cern.ch/Atlas/GROUPS/PHYSICS/PAPERS/EXOT-2016-19/.
Faculty search on ATLAS
The Department seeks an individual with outstanding research and a strong commitment to teaching. A PhD and postdoctoral experience in an area closely related to experimental high energy physics are required. To apply online, please go to http://umass.interviewexchange.com/jobofferdetails.jsp?JOBID=77002 and submit a cover letter, resume including key publications, research plan, teaching statement and contact information for three professional references. Applicants should apply by the priority deadline of December 1, 2016, in order to ensure consideration.
The university is committed to active recruitment of a diverse faculty and student body. The University of Massachusetts Amherst is an Affirmative Action/Equal Opportunity Employer of women, minorities, protected veterans, and individuals with disabilities and encourages applications from these and other protected group members. Because broad diversity is essential to an inclusive climate and critical to the University’s goals of achieving excellence in all areas, we will holistically assess the many qualifications of each applicant and favorably consider an individual’s record working with students and colleagues with broadly diverse perspectives, experiences, and backgrounds in educational, research or other work activities. We will also favorably consider experience overcoming or helping others overcome barriers to an academic degree and career.
We are seeking talented applicants qualified for an assistant professor position. Under exceptional circumstances, highly qualified candidates at other ranks may receive consideration.
LHC Run 2 start at 13 TeV
Run 2 of the LHC at the higher center of mass energy of 13 TeV has begun. It provides a unique opportunity for further discovery in the next few years thanks to the energy increase. For some additional information see the UMass press release at http://www.umass.edu/newsoffice/article/umass-amherst-physicists-eager-begin.